On May 2nd, Advanced Science published a collaborative study from Drs. Liu Jia, Jiang Biao Laboratories of Shanghai Institute for Advanced Immunochemical Studies (SIAIS) and Dr. Jiang Xianxing from the School of Pharmaceutical Science at Sun Yat-Sen University, entitled “Photoactivatable Fluorogenic Labeling via Turn‐On “Click‐Like” Nitroso‐Diene Bioorthogonal Reaction”. Their study develops nitroso-diene-based bioorthogonal fluorogenic reaction, providing new tools for chemical biology research.
By leaving free fluorophore untouched, fluorogenic labeling can minimize background signal when labeling protein of interest (POI). In the present study, Dr. Liu Jia and Jiang Biao Laboratories teamed up with collaborators to develop a highly efficient, bioothogonal nitro-based Diels-Alder (nDA) reaction for in vitro and in vivo fluorogenic labeling in cells. By UV light activation, the fluorescence of the nDA reaction can be further enhanced, thus allowing for the temporal control of fluorogenic reaction.
Dr. Bai Li from the School of Pharmaceutical Science at Sun Yat-Sen University and 2015 graduate student Zhou Xianhao from SIAIS at ShanghaiTech University are co-first authors of this study. Dr. Jiang Xianxing from the School of Pharmaceutical Science at Sun Yat-sen University and Dr. Liu Jia, the principle investigator of the Laboratory of Macromolecule Drug Delivery at SIAIS are the co-corresponding authors. This study was supported by the Major Research Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China and Guangdong Introducing Innovative Program.

Figure 1. Different fluorogenic approach for protein labeling. A. Fluorogenic labeling based on ligation reactions. B. Fluorogenic labeling based on a fluorescence quenching strategy. C. In situ generated light‐activatable probes via fluorogenic nitroso‐diene pairs.
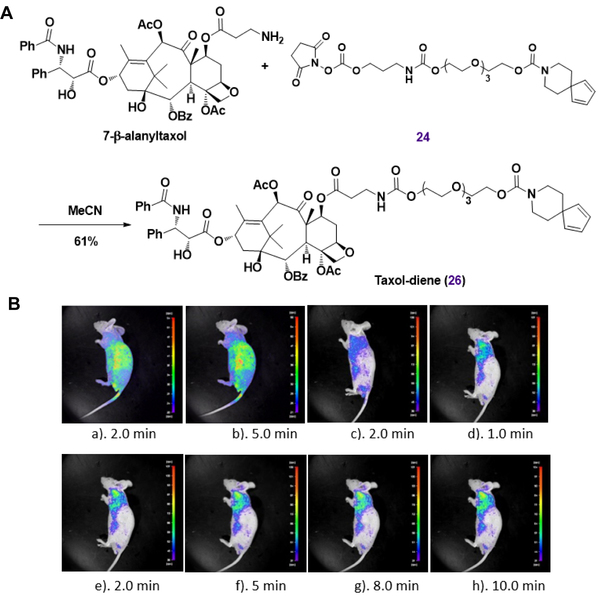
Figure 2. In vivo fluorescence imaging. A. Synthesis of diene‐bearing taxol. B. NIR images of living ZR‐75‐1 breast tumor model mice after tumor local injection of nitroso‐diene probe at different time points: a,b) Control fluorescence imaging for injection of fluorogenic probe pairs: the nontargeted diene (20) and 9 at 2.0 and 5.0 min points. c) Control fluorescence imaging for injection of taxol‐diene (26) at 2.0 min point. d–h) Fluorescence imaging for injection of fluorogenic probe pairs: taxol‐diene (26) and 9 at 1.0, 2.0, 5.0, 8.0, and 10.0 min points.

